Quiz
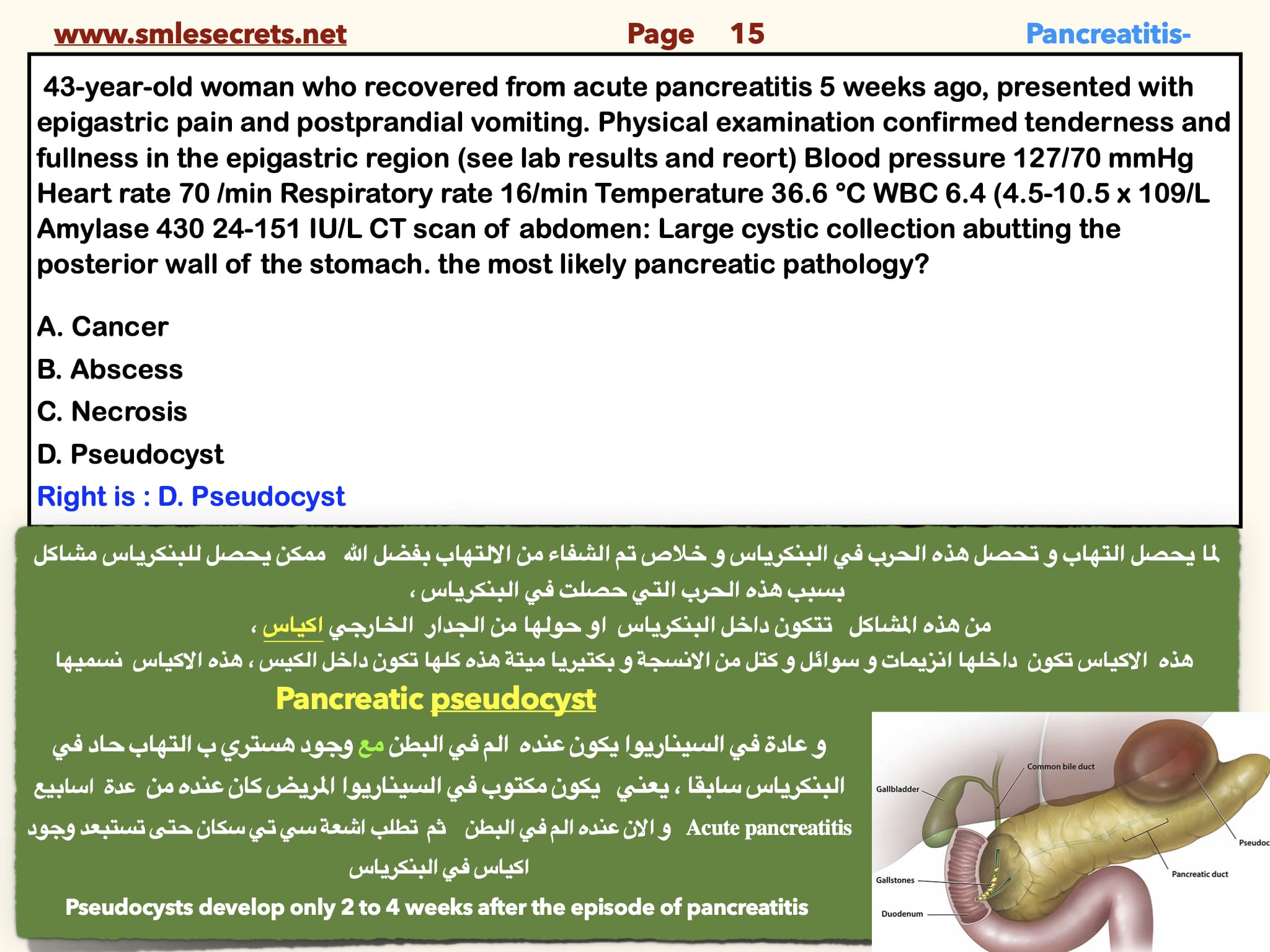
Q- A 43 year old woman who recovered from acute pancreatitis 5 weeks ago, presented with epigastric pain and postprandial vomiting. Physical examination confirmed tenderness and fullness in the epigastric region (see lab results and reort) Blood pressure 127/70 mmHg Heart rate 70 /min Respiratory rate 16/min Temperature 36.6 °C WBC 6.4 )4.5-10.5 x 109/L Amylase 430 24-151 IU/L CT scan of abdomen: Large cystic collection abutting the posterior wall of the stomach. the most likely pancreatic pathology
A. Cancer
B. Abscess
C. Necrosis
D. Pseudocyst
Right is : D. Pseudocyst
A 38-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department with epigastric pain and post-prandial vomiting. She was treated conservatively for acute pancreatitis 4 weeks ago. Physical Examination: Tenderness and fullness in the epigastric region Abdominal Ultrasound: Fluid collection surrounded by a thick wall in the lesser sac, measuring 15 x 17 cm. Amylase: 413 (Normal: 24–151 IU/L) WBC: 15.9 (Normal: 4.5–10.5 x 10⁹/L) What is the most likely diagnosis
A. Abscess
B. Phlegmon
C. Pseudocyst
D. Walled-off necrosis
Right is : C- Pseudocyst
A37-year-old woman complains of abdominal fullness, epigastric discomfort and loss of appetite, She is recovering from an episode of acute pancreatitis 5 weeks ago. On examination, her abdomen is distended and there is vague fullness in epigastrium CT scan: Cyst about 24 x 18 cm in the lesser sac. the most appropriate management?
A. Excision of cyst
B. Surgical drainage
C. Image guided aspiration
D. Endoscopic Internal drainage
Right is : D. Endoscopic Internal drainage
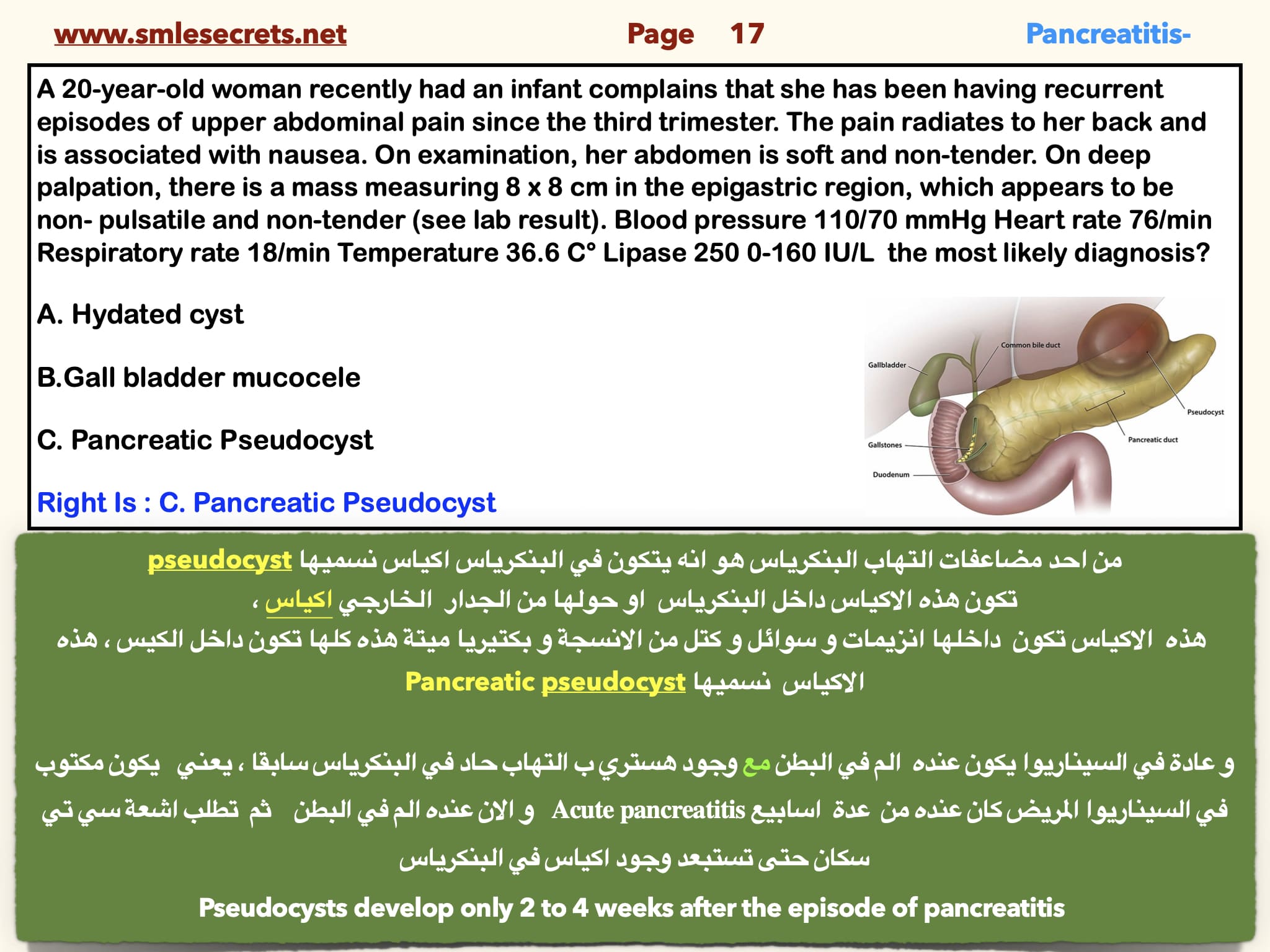
A 20-year-old woman recently had an infant complains that she has been having recurrent episodes of upper abdominal pain since the third trimester. The pain radiates to her back and is associated with nausea. On examination, her abdomen is soft and non-tender. On deep palpation, there is a mass measuring 8 x 8 cm in the epigastric region, which appears to be non- pulsatile and non-tender (see lab result). Blood pressure 110/70 mmHg Heart rate 76/min Respiratory rate 18/min Temperature 36.6 C° Lipase 250 0-160 IU/L the most likely diagnosis
A. Hydated cyst
B.Gall bladder mucocele
C. Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Right Is : C. Pancreatic Pseudocyst
A 41-year-old woman presented to the Emergency Department complaining of a 2-week history of upper abdominal pain associated with vomiting and fever. History reveals she underwent conservative treatment of acute hyperlipidaemia induced pancreatitis 6 weeks ago. Physical examination confirmed tenderness in the epigastric region Blood pressure 110/70 mmHg Heart rate 100/min Temperature 38.1 C° WBC 20.2 (4.5-10.5 x 109/L ) Amylase 245 (24-151 IU/L) Ultrasound: Well circumscribed collection (15 x 17 cm) in the lesser sac. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial method of drainage?
A. Endoscopic
B. Laparoscopic
C. Percutaneous
D. Open surgical
Right is : Percutaneous
A 24-year-old man recovers from an attack of severe pancreatitis. He has mild epigastric
discomfort, sensation of bloating, and loss of appetite. Examination reveals an epigastric
fullness. The swelling increases in size over a 3-week period of observation (see report).
Ultrasound: Confirmed to be a pseudocyst. the most appropriate next step ?
A. Observation
B. Internal drainage
C. Percutaneous drainage
D. Excision of pseudocyst
Right is: A. Observation
A60-year-old woman presents with a 12-hour history of severe pain in the epigastrium radiating to her back. It is associated with nausea and 2 episodes of vomiting. She has a history of cholelithiasis. Abdominal examination confirms generalized tenderness in abdomen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Biliary colic
B.Acute pancreatitis
C.Acute cholecystitis
D. Empyema gallbladder
Right is B.Acute pancreatitis
Q- A 40-year-old man with a history of hypertriglyceridemia presents to Emergency Room with 4-hour of sever epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting. The pain was steady and radiate to the back. The patient was in pain and agitated Blood pressure 100/70 mmHg Heart rate 110/min Respiratory rate 23 /mm Temperature 38.3 “C WBC 16 4.5-10.5 x 109/L
Alanine aminotransferase 97 5-40 IU/L Aspartate aminotransferase 87 12-40 IU/L
Amylase 150 24-151 IU/L Lactate dehydrogenase 169 60-160 IU/L
Lipase 30 0-160 IU/L Plain Abdominal X-ray: Showed an air-filled intestinal loop at left upper quadrant
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acute pancreatitis
A. Bowel perforation
B. Mesenteric ischemia
C. Diverticular disease
Right is : A. Acute pancreatitis
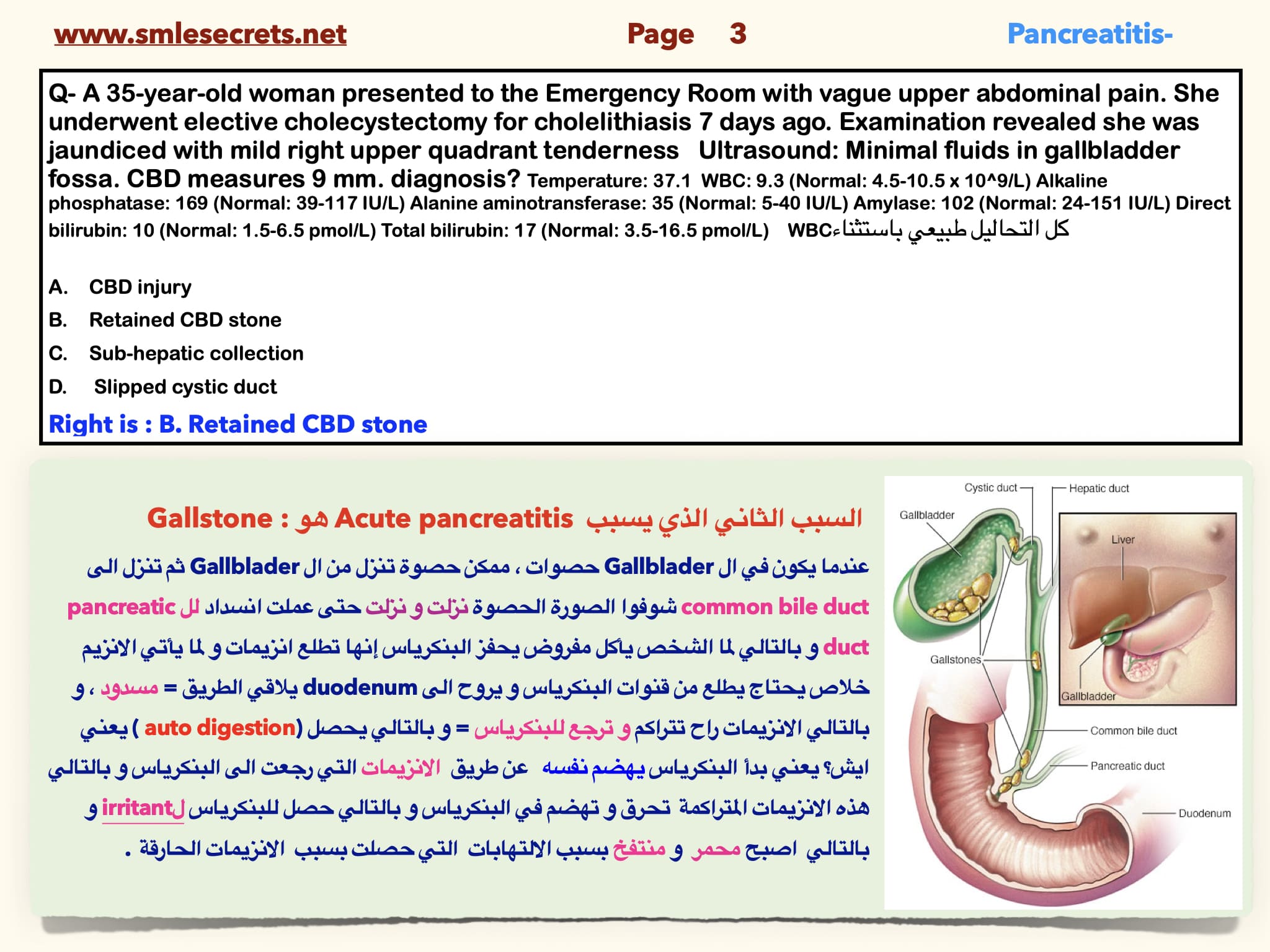
Q- A 35-year-old woman presented to the Emergency Room with vague upper abdominal pain. She underwent elective cholecystectomy for cholelithiasis 7 days ago. Examination revealed she was jaundiced with mild right upper quadrant tenderness Ultrasound: Minimal fluids in gallbladder fossa. CBD measures 9 mm. diagnosis? Temperature: 37.1 WBC: 9.3 (Normal: 4.5-10.5 x 10^9/L) Alkaline phosphatase: 169 (Normal: 39-117 IU/L) Alanine aminotransferase: 35 (Normal: 5-40 IU/L) Amylase: 102 (Normal: 24-151 IU/L) Direct bilirubin: 10 (Normal: 1.5-6.5 pmol/L) Total bilirubin: 17 (Normal: 3.5-16.5 pmol/L) WBCكل التحاليل طبيعي باستثناء
- CBD injury
- Retained CBD stone
- Sub-hepatic collection
- Slipped cystic duct
Right is : B. Retained CBD stone
A patient presents with abdominal pain lasting 16 hours, accompanied by nausea and vomiting. She has a known history of cholelithiasis. On physical examination, epigastric tenderness is noted. Lab Results: WBC: 13 (Normal: 4.5–10.5 x 10⁹/L) Amylase: 650 (Normal: 24–151 IU/L): What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Hepatitis
B. Acute pancreatitis
C. Acute cholecystitis
D. Perforated peptic ulcer disease
Right is : B. Acute pancreatitis
A28-year-old woman was admitted through the Emergency Department with a 12-hour history of epigastric pain. Physical examination confirmed epigastric tenderness. Over the next 3days during the hospitalization, the patient completely recovered clinically and biochemically Alkaline phosphatase 10 39-117 IUL/ Amylase 250 ) 24-151 IU/L ( Ultrasound: Multiple gallstones with mild extrahepatic biliary dilatation. Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention?
A- Abdominal computed tomography
B.Cholecystectomy before discharge
C. Interval cholecystectomy in 6-8 weeks
D. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
Right is : Cholecystectomy before discharge
A29-year-old woman presented ot the Emergency Department with an 8-hour history of severe epigastric pain radiating to the back associated with vomiting. She underwent a sleeve gastrectomy 3 months ago for morbid obesity. Physical examination confirmed mild epigastric tenderness (see lab results and report). Test Result Normal Values WBC 9.8 4.5-10.5 x 109/L Amylase 700 24-151 IU/L Ultrasound: Biliary sludge but no gallstone. Normal bile ducts. Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention?
A. Endoscopic ultrasound
B. Endoscopic sphincterotomy
C. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
D. Percutaneous cholecystostomy
Right is:C. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
45-year-old patient complains of recurrent episodes of upper abdominal pain for the past 2 week with fever. On examination, the patient is jaundiced, abdomen is soft with marked tenderness all over the abdomen Blood pressure 90/60 mmHg Heart rate 130/min Respiratory rate 18/min Temperature 38 °C Indirect bilirubin 5 3.2-12.1 pmol/L Direct bilirubin 20 1.5-6.5 umol/L Total bilirubin 25 3.5-16.5 pmol/L Alkaline phosphatase 450 39-117 IU/L Amylase 1400 24-151IU/L Ultrasound: CBD of 1.4 cm with dilatation of intra-hepatic ducts. diagnosis?
A. Hepatitis
B. Cholangitis
C. Pancreatitis
D. Acute Cholecystitis
Right is :C. Pancreatitis
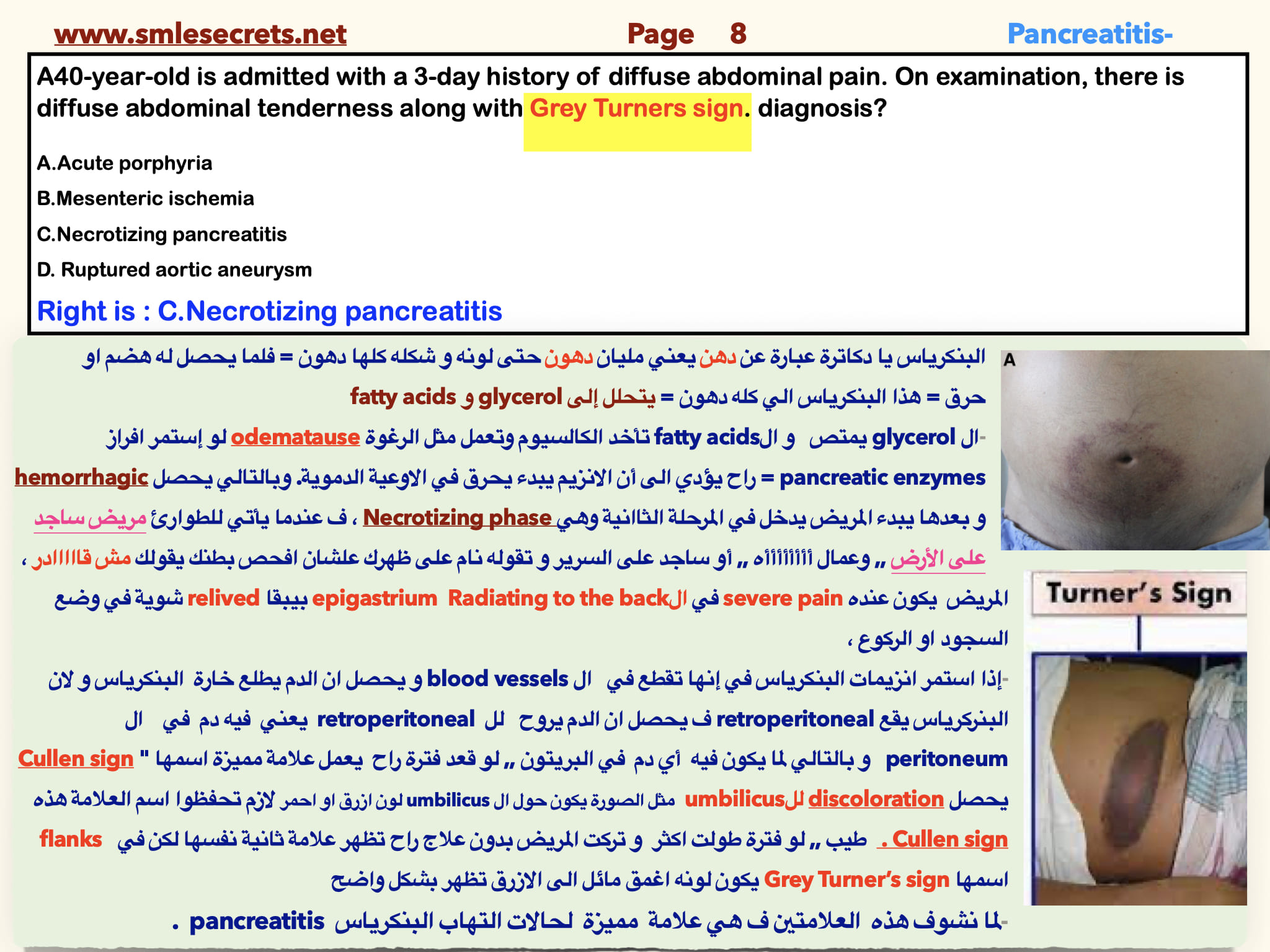
A40-year-old is admitted with a 3-day history of diffuse abdominal pain. On examination, there is diffuse abdominal tenderness along with Grey Turners sign. diagnosis?
A.Acute porphyria
B.Mesenteric ischemia
C.Necrotizing pancreatitis
D. Ruptured aortic aneurysm
Right is : C.Necrotizing pancreatitis
14 years old girl with epigastric pain for 2 days with nausea and vomiting. And absent from school. On examination, there upper abdominal distention and bruises. He had a history of fall of bicycle 18 days ago What is the most appropriate next step?
A- observation
B-Abdominal CT
C- laparoscopy
D- Abdominal US
Right is : B- Abdominal CT
A 42-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with a 12-hour history of severe epigastric pain. Physical examination reveals upper abdominal tenderness. Erect Chest X-Ray: Normal.
- WBC: 14.5 (Normal: 4.5–10.5 x 10⁹/L)
- Amylase: 254 (Normal: 24–151 IU/L)
What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Abdominal CT scan
B. Abdominal ultrasound
C. Exploratory laparotomy
D. Urine analysis for amylase
Right is : A. Abdominal CT scan
A 38-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department with epigastric pain for 6 days, radiating to the back and accompanied by frequent vomiting. She has a history of multiple small gallstones. Physical Examination:
- Diffuse abdominal distention + Epigastric tenderness + Sluggish bowel sounds
- Alkaline phosphatase: 115 (Normal: 39–117 IU/L) Direct bilirubin: 5.6 (Normal: 1.5–6.5 µmol/L)
- Amylase: 149 (Normal: 24–151 IU/L)
Erect Chest X-ray: Left pleural effusion What is the most appropriate initial investigation?
A. Trans-abdominal ultrasound
B. Urine analysis for amylase level
C. Abdominal computed tomography (CT)
D. Analysis of gastrointestinal aspirated fluids
Right is: C. Abdominal computed tomography (CT)
A 38-year-old man with a 10-year history of recurrent acute pancreatitis presents with a 12-hour history of frequent vomiting of fresh blood. Intravenous fluid resuscitation has been initiated.
Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Isolated bleeding fundal varices controlled by injection sclerotherapy.
-
- Ultrasound: Splenomegaly + Normal portal vein + Thrombosed splenic vein
What is the most appropriate management?
A. Splenectomy
B. Portacaval shunt
C. Distal splenorenal shunt
D. Sengstaken-Blakemore tube
Right is : A. Splenectomy
A 67-year-old man presents with a 2-month history of yellowish discoloration of his sclera and skin, accompanied by dark urine and pale stools. Examination Findings: Jaundiced appearance + Palpable, distended gallbladder
- Alkaline phosphatase: 421 (Normal: 39–117 IU/L)
- Direct bilirubin: 122.3 (Normal: 1.5–6.5 µmol/L)
- Total bilirubin: 134.5 (Normal: 3.5–16.5 µmol/L)
Ultrasound Report:
- Dilated intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts
- Hugely distended gallbladder
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Klatskin tumor
B. Pancreatic cancer
C. Mirizzi’s syndrome
D. Common bile duct stone
Right is : B. Pancreatic cancer
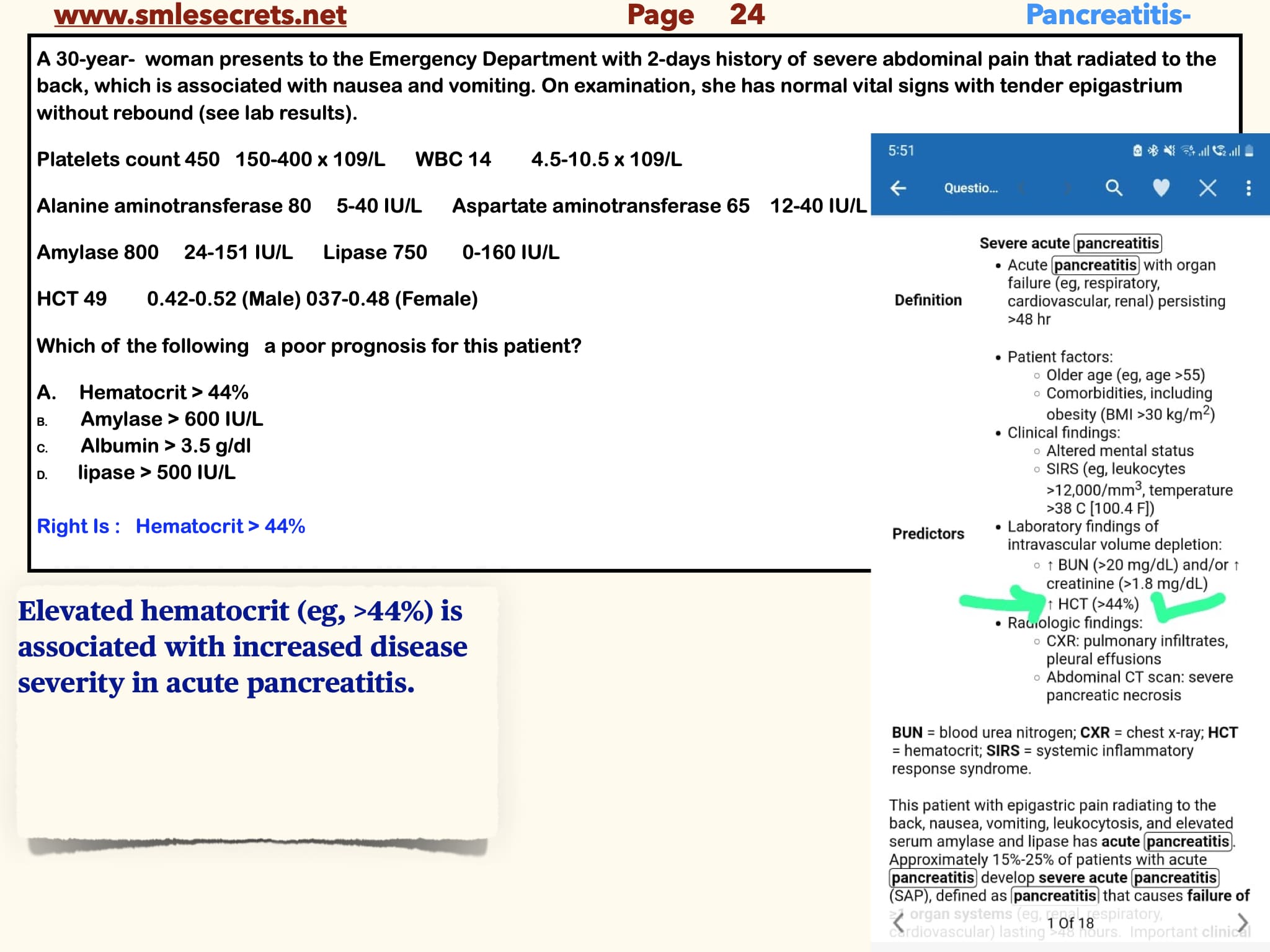
A 30-year- woman presents to the Emergency Department with 2-days history of severe abdominal pain that radiated to the back, which is associated with nausea and vomiting. On examination, she has normal vital signs with tender epigastrium without rebound (see lab results). Platelets count 450 150-400 x 109/L WBC 14 4.5-10.5 x 109/L Alanine aminotransferase 80 5-40 IU/L Aspartate aminotransferase 65 12-40 IU/L
Amylase 800 24-151 IU/L Lipase 750 0-160 IU/L
HCT 49 0.42-0.52 (Male) 037-0.48 (Female)
Which of the following a poor prognosis for this patient?
A- Hematocrit > 44%
B- Amylase > 600 IU/L
C- Albumin > 3.5 g/dl
D- lipase > 500 IU/L
Right Is : Hematocrit > 44%
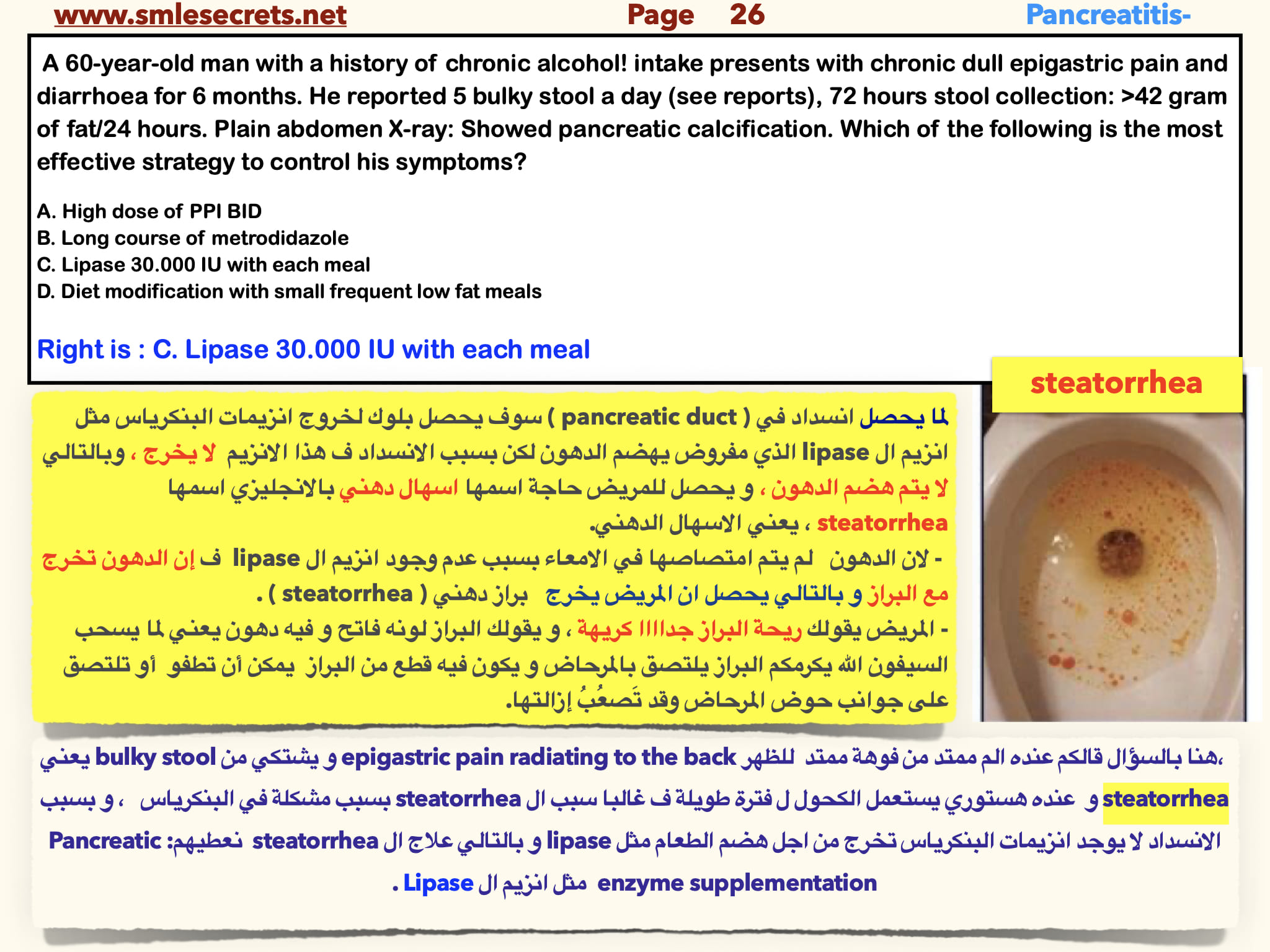
A 60-year-old man with a history of chronic alcohol! intake presents with chronic dull epigastric pain and diarrhoea for 6 months. He reported 5 bulky stool a day (see reports), 72 hours stool collection: >42 gram of fat/24 hours. Plain abdomen X-ray: Showed pancreatic calcification. Which of the following is the most effective strategy to control his symptoms?
A. High dose of PPI BID
B. Long course of metrodidazole
C. Lipase 30.000 IU with each meal
D. Diet modification with small frequent low fat meals
Right is : C. Lipase 30.000 IU with each meal
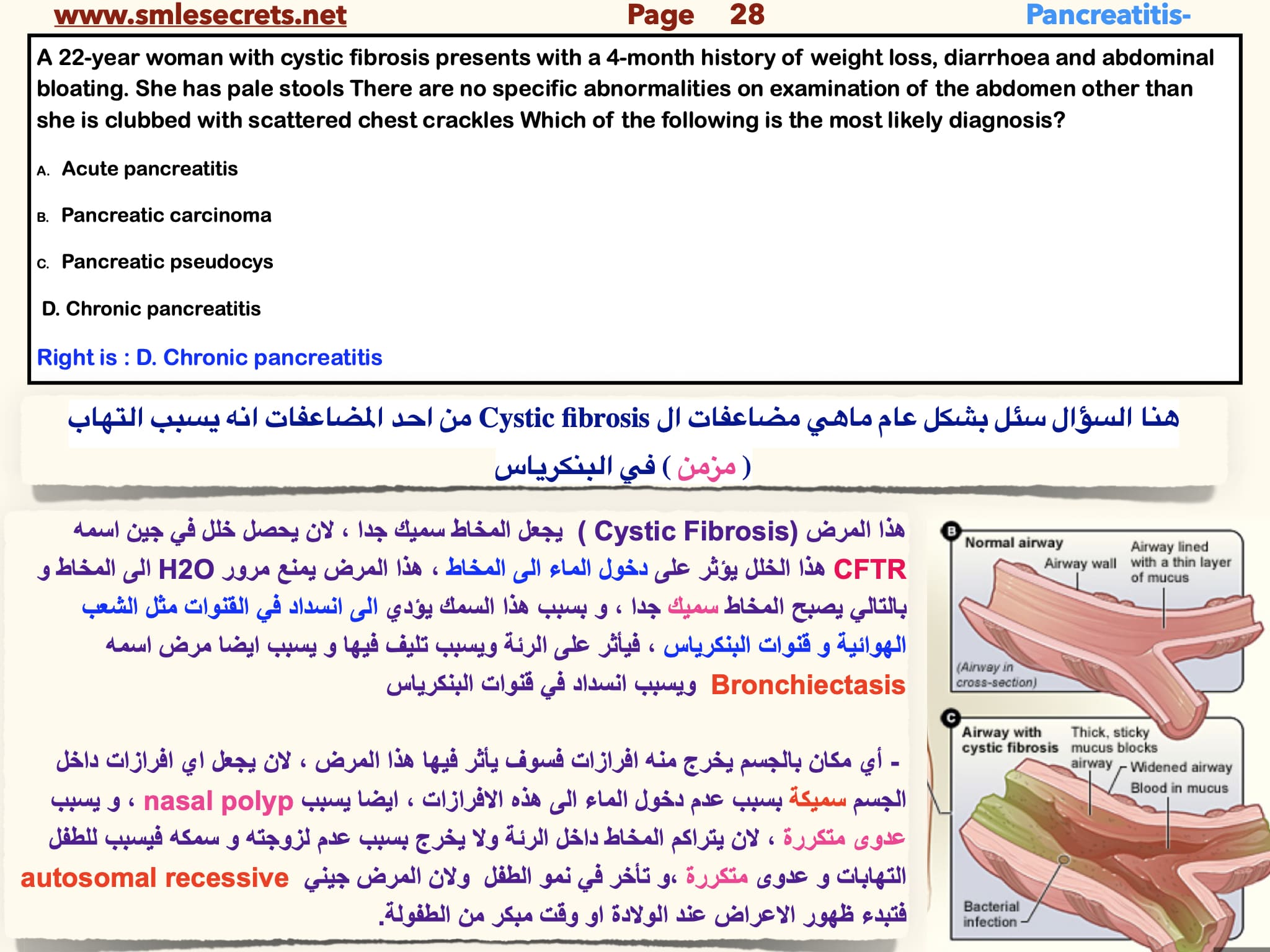
A 22-year woman with cystic fibrosis presents with a 4-month history of weight loss, diarrhoea and abdominal bloating. She has pale stools There are no specific abnormalities on examination of the abdomen other than she is clubbed with scattered chest crackles Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acute pancreatitis
B. Pancreatic carcinoma
C. Pancreatic pseudocys
D. Chronic pancreatitis
Right is : D. Chronic pancreatitis
A 35-year-Wd man has been in the Intensive Care Unit with severe pancreatitis, ventilator dependence, and pneumonia for 2 weeks. He is receiving nutrition parenterally (see lab results). Platelets count 184 normal( 150-400 x 109/L) Total bilirubin 4 , Normal ( 6 3.5-16,5 pmol’L) APTT 36 normal (30-40 sec) INR 2.1 normal (0.8-1 2) the most appropriate management?
- Factor X
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin C
- Factor VIII
Right is : Vitamin K
Q-27 years old male presented 4 weeks ago with severe necrotizing pancreatitis. He underwent several interventions for sepsis control and drainage. He was put on mechanical ventilation and inotropes What is he expected to have?
- Decreased gluconeogenesis.
- Increased lipolysis
- Hypoglycemia
- Decreased insulin resistance
Right is : Increased lipolysis